New Scorecard | Investment in child health saves 34 million children worldwide
On 4th July 2015, a new analysis was published in The Lancet entitled “Keeping score: fostering accountability for children’s lives”. The analysis reveals that more than 34 million children’s lives have been saved since 2000 because of investments in child health programmes. In the poorest…
On 4th July 2015, a new analysis was published in The Lancet entitled “Keeping score: fostering accountability for children’s lives”. The analysis reveals that more than 34 million children’s lives have been saved since 2000 because of investments in child health programmes. In the poorest countries, such as Tanzania and Haiti, the analysis calculates the cost of saving a child’s life is as little as $4,205.
This analysis, authored by the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington and the UN Secretary-General’s Special Envoy for Financing the Health Millennium Development Goals and for Malaria, builds off the work of an international collaboration of researchers.
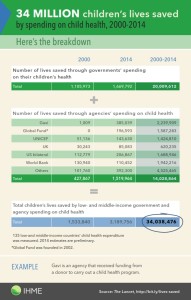 It also provides a scorecard that allows governments, policymakers, and donors to track investments in child health. Furthermore, the scorecard allows stakeholders to link those investments to child deaths averted across countries in a comparable manner.
It also provides a scorecard that allows governments, policymakers, and donors to track investments in child health. Furthermore, the scorecard allows stakeholders to link those investments to child deaths averted across countries in a comparable manner.
“If you invest in the poorest countries, you will see the biggest impact in child health because the costs of things like nutrition programmes, vaccines and primary care are lower.” – Christopher Murray, Director, Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation
IHME and the Special Envoy’s office hope that the scorecard will be further developed and updated annually to measure the effects of investments, incentivize progress, and drive innovation to fill gaps in funding or interventions.
Download the analysis: The Lancet
Learn more: Office of the UN Secretary-General’s Special Envoy for Financing the Health Millennium Development Goals and for Malaria & Department of Global Health – University of Washington